I still remember the frustration of trying to get a stable GPS signal in the city, only to be told that what is assisted gps (a-gps) was some kind of magical solution that would fix all my location-based problems. But let’s be real, most explanations of A-GPS sound like they’re written by engineers for engineers – _totally_ missing the point of why we need it in the first place. As someone who’s worked on designing chips for smartphones, I’ve seen firsthand how A-GPS can be a game-changer, but only if you understand how it actually works.
In this article, I promise to cut through the jargon and give you a no-nonsense explanation of what A-GPS is and how it can help your device find its way. I’ll draw from my own experience working with GPS technology to provide you with a clear, easy-to-understand guide to A-GPS. My goal is to empower you with knowledge, not to confuse you with technical terms – so, let’s dive in and explore the world of assisted GPS together, shall we?
Table of Contents
What Is Assisted Gps a Gps
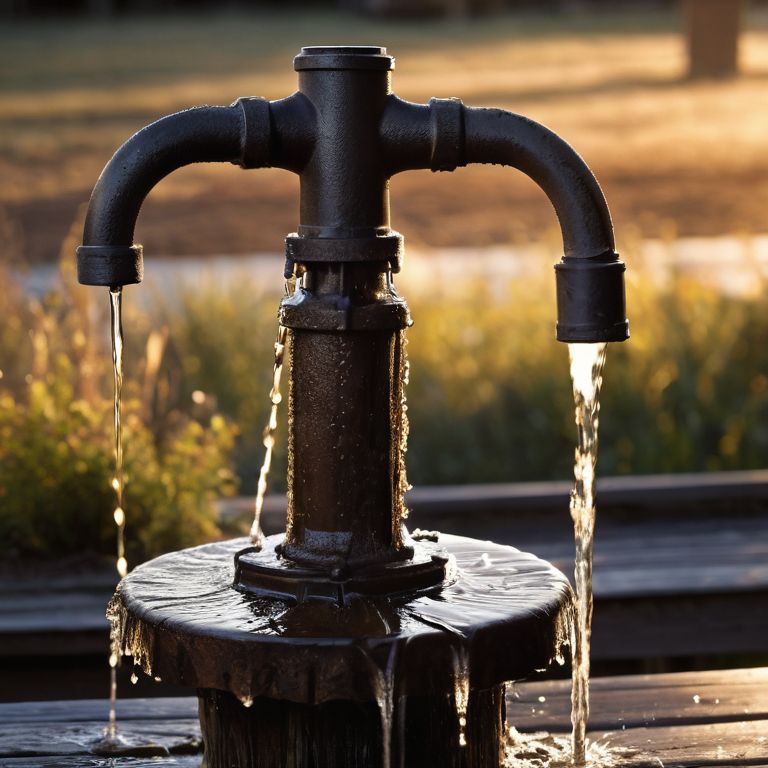

To understand how Assisted GPS, or A-GPS, works, let’s first consider the challenges of traditional GPS systems. GPS signal augmentation is necessary because satellites are very far away, and their signals can be weak, making it difficult for devices to detect them. This is where A-GPS comes in – it uses additional data sources to enhance the functionality of traditional GPS systems. Think of it like a plumbing system, where the water pressure (GPS signal) is boosted by a pump (A-GPS) to reach farther distances.
The benefits of assisted GPS are numerous. For one, it significantly improves the accuracy and speed of location-based services. This is achieved by using cellular network data or Wi-Fi signals to augment the GPS signal, allowing devices to determine their location more quickly and precisely. A-GPS vs GPS is not a competition, but rather a complementary relationship, where A-GPS fills in the gaps when traditional GPS is not enough.
In essence, A-GPS is a technology that supercharges your regular GPS by adding some extra helpers to get a more accurate location fix. By combining GPS data with other sources of information, such as cellular triangulation or Wi-Fi-based positioning, A-GPS enables devices to provide more accurate and reliable location-based services. This is particularly useful in areas with limited GPS coverage, such as urban canyons or indoors, where traditional GPS signals may be weak or unavailable.
Benefits of Assisted Gps Technology
When it comes to the benefits of Assisted GPS technology, one of the most significant advantages is the ability to provide faster location fixes. This is especially important in situations where a quick and accurate location is crucial, such as in emergency response situations.
The use of Assisted GPS technology also offers improved accuracy, even in areas with limited satellite visibility. This is because A-GPS uses additional data sources, such as cell towers and Wi-Fi signals, to help determine the device’s location, resulting in a more precise fix.
How a Gps Works Its Magic
To understand how A-GPS works, let’s consider it like a team effort to find your location. Your device is the leader, but it can’t do it alone, so it gets help from additional data sources like cell towers or Wi-Fi routers. This assistance enables your device to get a faster and more accurate location fix, even in areas with limited satellite visibility.
When your device uses A-GPS, it’s essentially combining signals from multiple sources to determine its location. This approach allows for better performance in challenging environments, such as urban canyons or indoors, where traditional GPS signals might be weak or unavailable.
A Gps vs Gps Signal Augmentation

When comparing A-GPS vs GPS, it’s essential to understand how they differ in terms of signal augmentation. Traditional GPS relies on satellites alone to provide location information, which can be affected by obstacles like buildings or trees. On the other hand, assisted GPS technology uses additional data sources, such as cell towers or Wi-Fi signals, to enhance the GPS signal and provide a more accurate location fix.
The benefits of assisted GPS become apparent in urban areas, where tall buildings and narrow streets can weaken GPS signals. By leveraging other signals, A-GPS can augment the GPS signal, allowing devices to maintain a stronger connection and provide more accurate location-based services. This is particularly useful for applications like navigation, where a strong signal is crucial for turn-by-turn directions.
In contrast to traditional GPS, which can be slow to acquire a signal, how A-GPS works allows it to quickly determine a device’s location, even in areas with limited satellite visibility. By combining GPS data with other signals, A-GPS can provide a faster and more accurate location fix, making it ideal for location-based services that require precise and timely information.
Gps Signal Augmentation Demystified
To understand how GPS signal augmentation works, imagine a plumbing system where water pressure is analogous to signal strength. Just as boosting water pressure can help it reach farther, signal amplification in A-GPS helps the GPS signal reach your device more clearly, even in areas with heavy interference or obstruction.
In this process, additional data from cell towers or satellites is used to assist the GPS signal, providing a more accurate location fix. This augmentation is crucial in urban areas where tall buildings can block or weaken GPS signals, making it difficult for devices to determine their exact location without assistance.
Location Based Services Explained
When we talk about location-based services, we’re referring to apps and features that use your device’s location to provide relevant information. This can include everything from mapping apps that give you turn-by-turn directions to social media platforms that show you nearby events.
The key to making these services work is accurate location data, which is where assisted GPS comes in. By providing a more precise location fix, A-GPS enables devices to deliver location-based services that are actually useful, rather than just giving you a general idea of where you might be.
Navigating the Basics: 5 Essential Tips for Understanding Assisted GPS (A-GPS)

- Know your surroundings: A-GPS uses additional data sources like cell towers and Wi-Fi hotspots to improve location accuracy, so it’s crucial to understand how these helpers work together
- Signal strength matters: The quality of the GPS signal your device receives can greatly impact A-GPS performance, making it essential to be in an area with a strong signal for the best results
- Assistance from the cloud: Many A-GPS systems rely on cloud-based data to provide location information, which means having a stable internet connection can enhance the overall performance of A-GPS
- Device compatibility is key: Not all devices are created equal when it comes to A-GPS, so it’s vital to check if your smartphone or tablet supports this technology for optimal use
- Understanding the limits: While A-GPS can significantly improve location services, it’s not foolproof – being aware of its limitations, such as urban canyon effects or indoor signal degradation, can help manage expectations and optimize its use
Key Takeaways: Unlocking the Power of Assisted GPS
Assisted GPS (A-GPS) enhances traditional GPS by leveraging additional data sources to provide more accurate and efficient location fixes, especially in challenging environments
A-GPS technology offers several benefits, including improved location accuracy, reduced power consumption, and faster time-to-first-fix, making it a crucial component in modern navigation systems
Understanding the differences between A-GPS and traditional GPS, as well as how signal augmentation works, can help you appreciate the complex technology behind location-based services and how they impact our daily lives
Unlocking A-GPS Secrets
Assisted GPS is like having a personal navigator who not only gives you directions but also helps you avoid traffic jams, taking the uncertainty out of finding your way, and making the journey smoother and more enjoyable.
Chloe Brennan
Conclusion: Unlocking the Power of Assisted GPS
As we’ve explored the world of Assisted GPS (A-GPS), it’s clear that this technology is more than just a fancy add-on to traditional GPS systems. By supercharging your device’s location-finding abilities, A-GPS provides a more accurate and reliable way to navigate the world. From understanding how A-GPS works its magic to exploring the benefits of assisted GPS technology, we’ve broken down the complex into the simple. We’ve also delved into the differences between A-GPS and traditional GPS, including the concept of signal augmentation and location-based services.
As you move forward, remember that technology is only as powerful as your understanding of it. Don’t be afraid to ask the question ‘how does it work?’ and seek out the answers. By demystifying the ‘black box’ of modern electronics, you’ll not only gain a deeper appreciation for the tech that surrounds you, but you’ll also unlock a world of possibilities and inspiration. So, go ahead and explore, create, and innovate – the world of A-GPS and beyond is waiting for you!
Frequently Asked Questions
How does Assisted GPS improve location accuracy in areas with limited satellite visibility?
Think of A-GPS like a plumbing system – it adds extra ‘water pressure’ to help your device find its location when regular GPS signals are weak. By using cellular network data and other assistants, A-GPS can pinpoint your location even in areas with limited satellite visibility, like urban canyons or indoors.
Can I use Assisted GPS on any device, or are there specific requirements?
So, can you use Assisted GPS on any device? Not quite – your device needs a cellular or internet connection to tap into those extra helpers. Think of it like a plumbing system, where A-GPS is the water pump that boosts the flow of location data, but you still need pipes (a connection) to make it work.
Does Assisted GPS consume more battery power than traditional GPS due to the additional data sources it utilizes?
Think of A-GPS like a team effort – it uses cellular networks and Wi-Fi to help GPS get a fix. While it’s true that A-GPS uses extra data, it actually ends up being more power-efficient in the long run, as it can get a location fix faster and more accurately, reducing the overall power consumption.